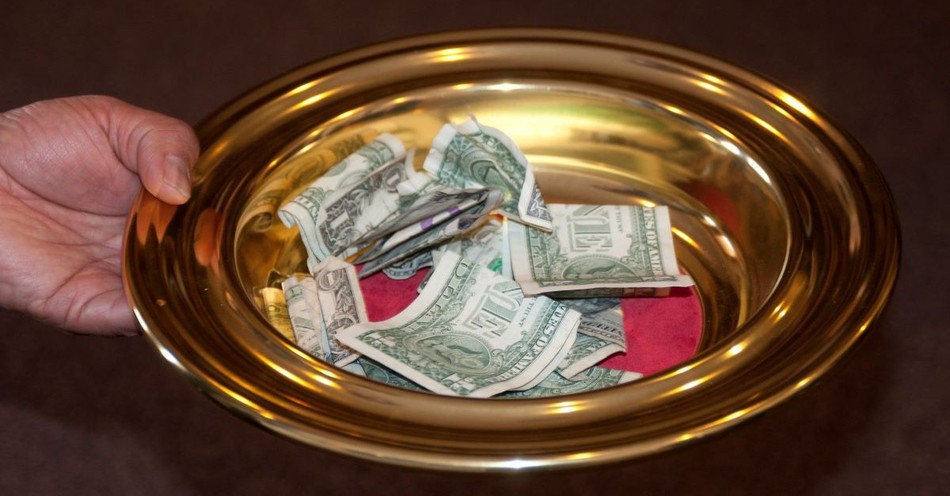
The term "tithe" is derived from the Old English word "teogotha," meaning "tenth." In biblical terms, tithing refers to the practice of giving 10% of one's income or resources to support the church or religious community. Tithing has a rich history, seen throughout both the Old and New Testaments.
What is a Tithe? Table of Contents
- Definition of a Tithe
- Tithing in the Old Testament
- Tithing in the New Testament
- Historical Context of Tithing in Other Religions
- Theological Debates and Interpretations of Tithing
- Impact of Tithing on Church Finances and Programs
- Psychological and Social Benefits of Tithing
- Challenges and Criticisms of Tithing
- Modern Alternatives to Traditional Tithing
- Scriptural Interpretations and Variations
- The Significance of Tithing
- Contemporary Practices of Tithing
- Tithing in the Bible
Definition of a Tithe
The term "tithe" means "tenth." Tithing refers to the practice of giving 10% of one’s income or resources to the church or religious community. It is an act deeply rooted in biblical traditions and is mentioned throughout the Old and New Testaments.
Tithing in the Old Testament
Abraham's Tithe: Abraham offered a tenth of his spoils of war to the priest Melchizedek (Genesis 14:18-20).
Mosaic Law: Under Mosaic Law, the Israelites were required to give a tenth of their crops, livestock, and income as an offering to the Lord, which supported the Levites (Leviticus 27:30-32).
Malachi's Message: The prophet Malachi urged Israel to tithe faithfully to experience God's blessings (Malachi 3:10).
Tithing in the New Testament
Although the New Testament does not command tithing in the same way as the Old Testament, it emphasizes generosity and giving from the heart. Jesus praised the widow’s offering as an act of true faith (Mark 12:41-44), and Paul encouraged cheerful, voluntary giving (2 Corinthians 9:7).
Historical Context of Tithing in Other Religions
Similar practices exist in Judaism, where tithing, or "Ma'aser," is required by the Torah, and in Islam, where "Zakat" is an obligation to give 2.5% of wealth to the poor. Both emphasize social welfare and the importance of supporting religious duties.
Theological Debates and Interpretations of Tithing
Within Christianity, there are differing views on tithing. Some see it as a mandatory Old Testament law, while others believe it should be a voluntary act based on New Testament principles of generosity. Whether it should be a fixed 10% or more flexible remains a subject of debate.
Impact of Tithing on Church Finances and Programs
Tithing is crucial for sustaining church operations, supporting clergy, and funding mission trips, charitable activities, and ministries. Churches often rely heavily on tithes for their financial health.
Psychological and Social Benefits of Tithing
Tithing fosters community and purpose. It helps individuals feel fulfilled and connected, knowing their contributions are helping the church and wider community. It promotes collective responsibility and care for others.
Challenges and Criticisms of Tithing
Tithing can be burdensome for those with limited financial means, and concerns about misuse of funds may lead to skepticism. Transparency and accountability are essential to maintaining trust in how tithes are used.
Modern Alternatives to Traditional Tithing
In the digital age, churches are adopting new ways for congregants to give. Digital giving platforms and crowdfunding for specific church projects are popular alternatives, especially among younger generations.
Scriptural Interpretations and Variations
Different denominations interpret tithing differently. Some emphasize Old Testament law, while others focus on the New Testament’s encouragement for voluntary, cheerful giving. These variations reflect broader theological perspectives.
The Significance of Tithing
- Obedience and Trust: Tithing demonstrates obedience to God and trust in His provision.
- Supporting Ministry and Outreach: Tithing enables churches to sustain their ministries and outreach programs.
- Blessings and Gratitude: Tithing expresses gratitude to God for His blessings and provision.
Contemporary Practices of Tithing
While tithing traditionally refers to giving 10% of one’s income, modern tithing can extend beyond finances. Many believers tithe their time and talents by volunteering in their church communities.
Tithing in the Bible
The Bible’s teachings on tithing begin with Abraham’s offering and extend through Mosaic Law, the prophets, and into the New Testament. While the New Testament does not require a strict 10% tithe, it encourages generous giving from the heart, supported by examples like the widow’s offering and Paul's teachings on cheerful giving (2 Corinthians 9:7).
Conclusion
Tithing is a practice that has evolved over time, continuing to play a significant role in Christian faith and stewardship. It reflects obedience, gratitude, and support for the church and its mission. While the New Testament emphasizes giving willingly, tithing remains a meaningful way for Christians to participate in their faith and contribute to their community.
Photo Credit: ©GettyImages/MARIAMARTAGIMENEZ
This article is part of our Christian Terms catalog, exploring words and phrases of Christian theology and history. Here are some of our most popular articles covering Christian terms to help your journey of knowledge and faith:
The Full Armor of God
The Meaning of "Selah"
What Is Grace? Bible Definition and Christian Quotes
What is Discernment? Bible Meaning and Importance
What Is Prophecy? Bible Meaning and Examples

_639003522088907085.jpg)